Hello, my name is Lee Tze Shawn. One of my subject I have chosen for the IB syllabus is Maths Analysis and Approaches Higher Level (MAAHL). MAAHL is a very challenging subject but I will try my best.
Lev Vygotsky’s Theory
Vygotsky, a Soviet psychologist, known for his work on psychological development in children believed strongly that “learning is a necessary and universal aspect of the process of developing culturally organised, specifically human psychological function” and community plays a central role in the process of “making meaning.” Hence Vygotsky claimed that culture/language plays a powerful role in shaping thought and cognitive development varies across cultures/languages. Vygotsky defined the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) as the gap between our pre-existing development and what we can accomplish with the help of others, usually the More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) who are people with higher learning capacity and have more knowledge than the students. In addition, he purports that proper instruction and guidance from the MKO helps improve a child’s ability through the ZPD as he learns and remembers new skills.
The IB’s “Approaches to Learning” include:
- Thinking Skills: The ability to creatively and critically analyse, apply, evaluate, synthesise, conceptualise, contextualize, reason, and solve problems.
- Communication Skills: The ability to produce and interpret messages effectively.
- Social Skills: The ability to participate and collaborate with others whilst showing awareness and respect for other cultures, varying points of view, and individual differences.
- Research Skills: The ability to determine the extent of information needed, locate and access information, organise and evaluate information, and use and share information effectively, efficiently, and ethically.
- Self-management Skills: The ability to set goals, manage time and tasks effectively, and manage your state of mind, self-motivation, resilience, and mindfulness.
How Lev Vygotsky’s Social Learning Theory is Related to IB’s “Approaches to Learning”
Lev Vygotsky’s Social Learning Theory is related to the IB’s “Approaches to Learning” in a couple of ways. Firstly, Lev Vygotsky’s Social Learning Theory develops our thinking skills and communication skills because we are encouraged to seek the guidance of a More Knowledgable Other (MKO). Since two (or more) brains are better than one, the learner can use the newfound knowledge to think creatively and analyse them in greater depth. In addition during discussions with the MKO(s), the social and research skills are further enhanced as well. Similar to the communication skills, the learner can actively socialise with the MKO to clarify existing doubts, leading to more leads and motivation to conduct deeper analysis and further research. Lastly, the self-management skills of the learner are improved because the task is broken down into smaller achievable tasks, and with the guidance of the MKO the learner is fuelled with more motivation to complete the task with the best of his effort.
Sequences and Series Toolkit
Three Investigations (and a Bonus video presentation!)
Investigation 1 (partner discussion)


Q1)


Q2)


Q3)


Q4)
A 2D coordinate system specifies all points in the x-coordinate axis and the y-coordinate axis. A 3D coordinate system specifies all points in the x-coordinate axis, y-coordinate axis, and the z-coordinate axis. The difference between 2D coordinates and 3D coordinates is, there is one additional z-coordinate axis in 3D coordinates compared to 2D coordinates.
Q5)

Q6)

√(4)2 + (4)2 = √32
= 5.656854249
= 5.66 cm (to 3sf)

√[(√32)2 + (4)2] = √48
= 6.92820323
= 6.93 cm (to 3sf)
Q7)

√(4-4)2 + (2-2)2 + (2-0)2 = 2cm

√(2-2)2 + (0-0)2 + (4-2)2 = 2cm
Q8)
In my opinion, the understanding of 2D geometry is the building blocks to understanding 3D geometry. By starting out with 2 axises in 2D geometry, it helps develop the necessary visualisation and spatial reasoning skills to further proceed to 3D geometry since there is an additional z-coordinate axis.
Investigation 2

Q1) Let the area of the circle be A.
A= πr2
dA/dr = 2πr
Q2: Let the volume of a sphere be V
V = 4/3 πr3
dV/dr = 4πr2
Q3) In the case of squares, the first derivative of the area [of the given square, which is (2r)2 = 4r2] is equal to its surface area [8r]. In the case of cubes, the first derivative of the volume of the cube is equal to its surface area.
Q4)
Let the area of the square be A.
A = (2r)2
= 4r2
Let the volume of the cube be V.
V = (2r)3
= 8r3
Q5)
Let the perimeter of the square be P.
P = dA/dr = d(4r2)/dr
= 8r
Let the surface area of the cube be SA.
SA = dV/dr = d(8r3)/dr
= 24r2
Q6) The relationship between the circumference and area of a 2D object is, the circumference is the first derivative of the area. The relationship between the volume and surface area of a 3D object is, the surface area is the first derivative of the volume.
Investigation 3

Q1)

Q2)
Circumference: 2πr =2π(2.5cm) = 5π cm
Q3)
| Central angle in degrees | Length of corresponding arc (cm) |
| 360 ° | 5π |
| 180 ° | 2.5π |
| 90 ° | 1.25π |
| 60 ° | 56π |
| 45 ° | 0.625π |
| 30 ° | 512π |
Q4)
Radian is an alternate unit to measure angles. We can write radian in terms of degrees, where 1 radian is 180π°.
Q5)
| Central angle in degrees | Length of corresponding arc |
| 360 ° | 2πr |
| 180 ° | πr |
| 90 ° | (π/2)r |
| 60 ° | (π/3)r |
| 45 ° | (π/4)r |
| 30 ° | (π/6)r |
Q6)
s=rθ
Q7)
The ratio of the arc length and the radius have the same unit of measurement, so the units cancel out.
Group Video Presentation of Toolkit
Partner Discussion of Developing Inquiry Skills

Prior to the solving of this question, I had a zoom meeting with my partner as the both of us collaboratively analysed and discussed how to solve this question. One difficulty we encountered is, the variable ‘a’ is purposefully omitted in the question to stump us students, but included in the formula Volume = (4/3)(π)(r)2(a). Nonetheless the both of us found another formula on the internet and attempted to solve the question.
Formula of volume of a spheroid: 4/3 (π)(Vertical radius) * (Horizontal radius)2
Vertical radius (c) = 6m/2 = 3m
Horizontal radius (a) = 8m/2 = 4m
Volume of spheroid = 4/3 (π)(4m) * (3m)2
= 48π m3
= 150.7964474 m3
= 151 m3 (to 2sf)
Real Life Applications of Numbers, Algebra, Geometry and Trigonometry
- Real Life Application of Numbers and Algebra: Calculating the shopping bill.
Let the cost of an Economics Textbook be $w.
Let the cost of a Physics Textbook be $x.
Let the cost of a Chemistry Textbook be $y.
Let the cost of a Maths Textbook be $z.
My total bill can be expressed algebraically as: (1)($w) + (1)($x) + (1)($y) + (1)($z).
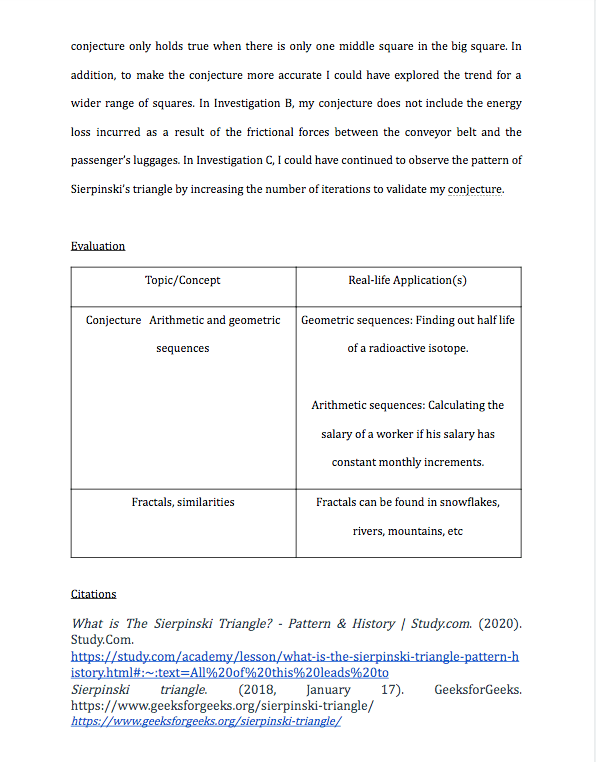
2. Real Life Application of Geometry: Mapping. Mapping is essential in jobs like surveying, navigation and astronomy. In addition medical professions benefit from geometric imaging, such as CT scans and MRIs.
3. Real Life Application of Trigonometry: Flight engineering. Trigonometry helps predict the behaviour of plane travel and landing given the variables of plane speed, distance travelled, and the direction and speed of the wind. For example, if a plane is travelling at 300 mph, 45 degrees Northeast, and there is a wind blowing due south at 25 mph. Solving for the third side of the triangle using trigonometry will lead the plane to the right direction.
International Mindedness
Waclaw Sierpinski (1882 – 1969) invented the Sierpinski’s triangle and it was named after him. Waclaw Sierpinski made important breakthroughs in the field of fractal dimensions, which lead to the discovery of the well-known Sierspinski’s triangle (analysis of this can be seen above).


5 IB learner profiles
Communicators: Discussion with partner allowed the both of us to express our views, collaborate effectively and accept each other’s point of view and analysis.
Principled: Citing the sources used for this assignment is a reflection of the IB learner profile of being principled – acting with integrity and honesty, with a strong sense of justice and fairness.
Risk-Takers: During the discussion with my partner, we had to take some risks to get started, then slowly eliminating conjectures that doesn’t make any sense at all while acquiring new knowledge and replacing initial doubts.
Balanced: Wise time management (also known as not procrastinating) to complete all other assignments that the average IB student is flooded with, including this one while still putting in dedication and effort.
Thinkers: Being good Communicators and Risk-takers isn’t enough. My partner and I both analysed how our ideas could relate to the solving of the investigations, which lead to the completion of this eJournal assignment.
References:
- https://www.ibo.org/contentassets/ef4f3c159e21444a9727ef9b7555681c/saturday-2pm—implementing-ib-approaches-to-learning—edward-lawless.pdf
- https://www.ipracticemath.com/learn/algebra/algebra_in_daily_life
- https://www.teach-nology.com/teachers/subject_matter/math/geometry/#:~:text=Also%2C%20geometry%20is%20used%20in,medicine%20benefit%20from%20geometric%20imaging.
- https://www.mathnasium.com/real-life-applications-of-trigonometry#:~:text=Trigonometry%20can%20be%20used%20to%20roof%20a%20house%2C%20to%20make,its%20applications%20in%20satellite%20systems.
- https://www.web-formulas.com/Math_Formulas/Geometry_Volume_of_Ellipsoid.aspx
- https://www.utdallas.edu/atec/midori/Handouts/coord_system.htm#:~:text=A%202D%20coordinate%20system%20is,all%20locations%20in%203D%20space.&text=In%20a%202D%20Cartesian%20coordinate,as%20(x%2C%20y).
- https://www.mathnasium.com/real-life-applications-of-trigonometry#:~:text=Trigonometry%20can%20be%20used%20to%20roof%20a%20house%2C%20to%20make,its%20applications%20in%20satellite%20systems.
- http://mathematica.ludibunda.ch/mathematicians12.html
Bibliography
Pamoja. (n.d.). Retrieved from Implementing IB Approaches to Teaching and Learning in a virtual environment: https://www.ibo.org/contentassets/ef4f3c159e21444a9727ef9b7555681c/saturday-2pm—implementing-ib-approaches-to-learning—edward-lawless.pdf
iPracticeMath. (n.d.). Algebra in Everyday Life. Retrieved from iPractice Math: https://www.ipracticemath.com/learn/algebra/algebra_in_daily_life
teAchnology. (n.d.). teAchnology. Retrieved from What is Geometry? When Do You Use It In The Real World?: https://www.teach-nology.com/teachers/subject_matter/math/geometry/#:~:text=Also%2C%20geometry%20is%20used%20in,medicine%20benefit%20from%20geometric%20imaging.
Mathnasium. (n.d.). Real life applications of trigonometry. Retrieved from Mathnasium: https://www.mathnasium.com/real-life-applications-of-trigonometry#:~:text=Trigonometry%20can%20be%20used%20to%20roof%20a%20house%2C%20to%20make,its%20applications%20in%20satellite%20systems.
WEB FORMULAS. (n.d.). WEB FORMULAS. Retrieved from Web-Formulas.com: https://www.web-formulas.com/Math_Formulas/Geometry_Volume_of_Ellipsoid.aspx
Utdallas.edu. (n.d.). Coordinate Systems. Retrieved from https://www.utdallas.edu/atec/midori/Handouts/coord_system.htm#:~:text=A%202D%20coordinate%20system%20is,all%20locations%20in%203D%20space.&text=In%20a%202D%20Cartesian%20coordinate,as%20(x%2C%20y).
Mathnasium. (n.d.). Mathnasium. Retrieved from Real life applications of trigonometry: https://www.mathnasium.com/real-life-applications-of-trigonometry#:~:text=Trigonometry%20can%20be%20used%20to%20roof%20a%20house%2C%20to%20make,its%20applications%20in%20satellite%20systems.
Anonymous. (n.d.). Retrieved from Mathematicians Benoit B.Mandelbrot and Waclaw Sierpinski: http://mathematica.ludibunda.ch/mathematicians12.html